General Information
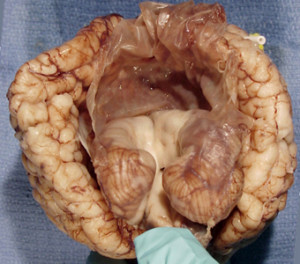
- The Dandy-Walker syndrome is hydrocephalus associated with a posterior fossa cyst and abnormal development of the cerebellum, a portion of the brain located near the base of the skull and important to voluntary muscle movement, balance and posture.
- This malformation occurs when openings that allow cerebrospinal fluid to move into the space surrounding the surface of the brain fail to open. The condition may prompt any of a number of brain and central nervous system abnormalities.
- Hydrocephalus occurs in 90 percent of cases.
Symptoms
- Symptoms of the Dandy-Walker syndrome depend to some extent on the combination of developmental difficulties in the infant. Increasing head size due to hydrocephalus may be the sole symptom.
- The normal signs of increased intracranial pressure may be absent in infants because of the head’s ability to grow. In older children, difficulties with balance, mental impairment and double vision can occur.
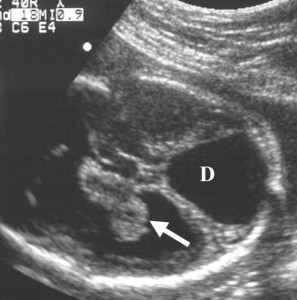
Diagnosis
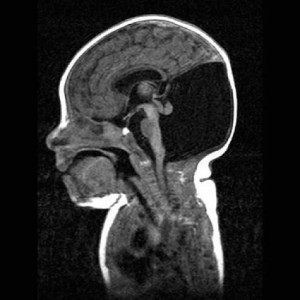
- Ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) will show the malformation.
Treatment
- When treatment is necessary, the posterior fossa cyst needs to be shunted to allow proper flow of cerebrospinal fluid. If there is no communication between the posterior fossa cyst and the lateral ventricles, then the lateral ventricles need to be shunted also.
Outcome
The chance of survival is 75 percent to 100 percent. About half of patients have nor
Consider using this space to introduce your page. Just click to add your own content.