Introduction
Introduction
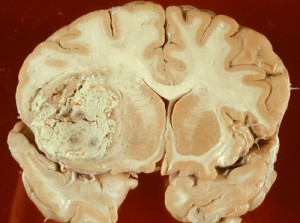
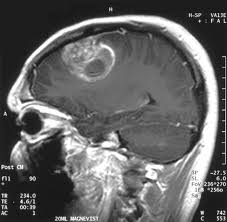
Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) is the most malignant type of astrocytoma (Grade 4astrocytoma). The most common tumor of the central nervous system (CNS), Glioblastomas account for 15 percent to 20 percent of CNS tumors but just 0.85 to 2 percent of all primary brain tumors.
Glioblastomas usually occur in patients older than 50 and rare in patients younger than 30.
Symptoms
- Glioblastoma symptoms may include seizure, focal neurologic deficit (weakness or speech problems), headaches, personality changes and visual loss.
Diagnosis
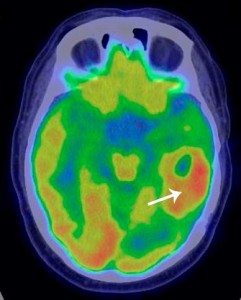
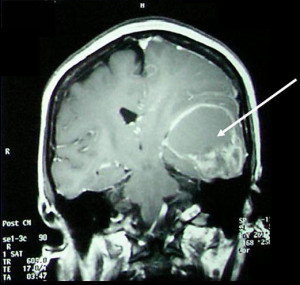
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the preferred imaging technique for diagnosis.
- An actual tissue biopsy is typically required for definitive diagnosis.
Glioblastoma Treatment
We use a multidisciplinary team approach to offer state-of-the-art treatment regimens of both standard and experimental treatments.
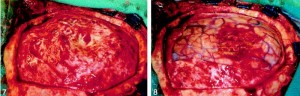
- Glioblastoma Surgery
- If possible, we attempt to remove all cancerous tissue visible on the MRI to relieve pressure on the surrounding brain and improve the effectiveness of certain additional therapies.
- Advanced technologies, such as neuronavigation and functional brain mapping and CUSA are available in our Hospital, may improve surgical outcome.
- Radiation therapy
- Six weeks of radiation therapy usually follows surgery.
- Stereotactic radiotherapy (using the TrueBeam Novalis system) may be offered in certain circumstances.
- Chemotherapy
- Standard oral chemotherapy, such as temozolomide is generally given during the radiation treatment, with additional doses afterward.
- Wafers loaded with chemotherapy (Gliadel) can be placed at the time of surgery. Ask your neurosurgeon and/or neuro-oncologist about this prior to surgery.
- Clinical research trials
- we offer many of the latest multicenter clinical trials available for glioblastoma.