Introduction
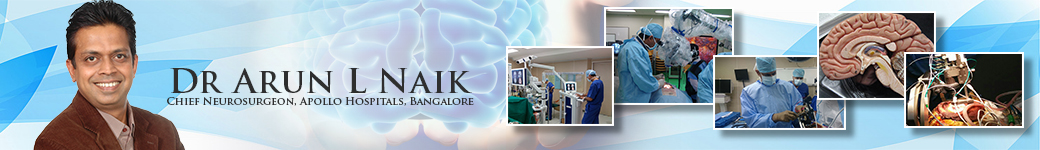
Ependymomas are a type of glioma, along with astrocytomaand oligodendroglioma. These tumors can occur anywhere in the brain or spinal cord. The most common site in the brain is at the bottom of the brain near the spinal cord. These tumors have the potential to spread through the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to other areas of the nervous system.
Symptoms
- Common symptoms include headache, nausea/vomiting, ataxia (difficulty with balance) or dizziness.
Diagnosis
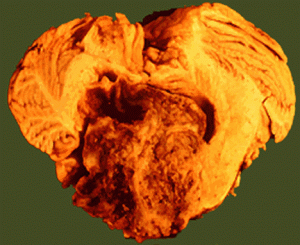
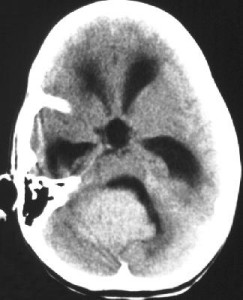
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the preferred diagnostic tool, although the diagnosis should be confirmed by microscopic examination of the tumor from a biopsy.
Treatment
- We offer a multidisciplinary management of ependymomas, with experts in neurosurgery, radiation oncology, and neuro-oncology working closely together to assure the highest quality of care.
- Surgery
- We will determine with you how much of the tumor can and should be removed.
- If the tumor is surgically accessible, a “complete” removal is attempted.
- An actual tissue biopsy is typically required for definitive diagnosis in nearly all cases.
- Sometimes, ependymomas are best removed with the aid of Neuronavigation surgery, allowing the most complete, safest surgery possible.
- Radiation Therapy
- Radiation therapy is administered to the tumor bed after surgical removal and if any metastases through the CSF are found.
- Chemotherapy
- We offer the latest in promising medical therapies available.
- Surgery